Weekly Reading List: Feb 24, 2025
Roche Announces SBX Technology, Creates Sequencing Buzz
Roche introduces Sequencing by Expansion (SBX) technology in a webinar just a few days before the AGBT meeting takes place in Florida.
Sequencing by Expansion SBX | Nanopore sequencing
Sequencing by expansion (SBX) offers a new paradigm in next-generation sequencing platform technology to expand capabilities beyond current nanopore sequencing.

Introducing sequencing by expansion (SBX): a versatile, high-throughput single-molecule sequencing technology

Opportunistic genomic screening has clinical utility: An interventional cohort study
Practice is shifting toward genome-first approaches, such as opportunistic screening for secondary findings (SFs). Analysis of SFs could be extended beyond medically actionable results to include non-medically actionable monogenic disease risks, carrier status, pharmacogenomic variants, and risk variants for common complex disease. However, evidence on the clinical utility of returning these results is lacking.
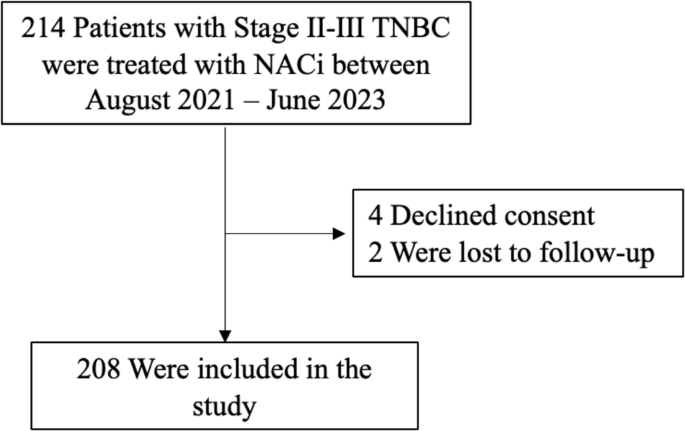
Clinico-pathological factors predicting pathological response in early triple-negative breast cancer - npj Breast Cancer
npj Breast Cancer - Clinico-pathological factors predicting pathological response in early triple-negative breast cancer
Roche Ripple Predictions
In the prior piece , I covered the technical details unveiled by Roche for their SBX technology, but generally tried to avoid predicting its…

U.S. early-career researchers struggling amid chaos
Uncertain funding, government firings, and distressed universities hit vulnerable groups especially hard
A Vaccine For Pancreatic Cancer Continues To Show Promise
In a small trial, nearly half of pancreatic cancer patients who received an mRNA vaccine for the disease had no relapse three years later.
Rare genetic disorder treated in womb for the first time
The child, who is now almost three years old, shows no signs of the often fatal motor neuron disease.
Fragile X Phenotypes Reversed in Mice by Targeting NMDA Receptors
MIT researchers suggests a potential molecular strategy for treating fragile X syndrome by enhancing NMDA subunit function.
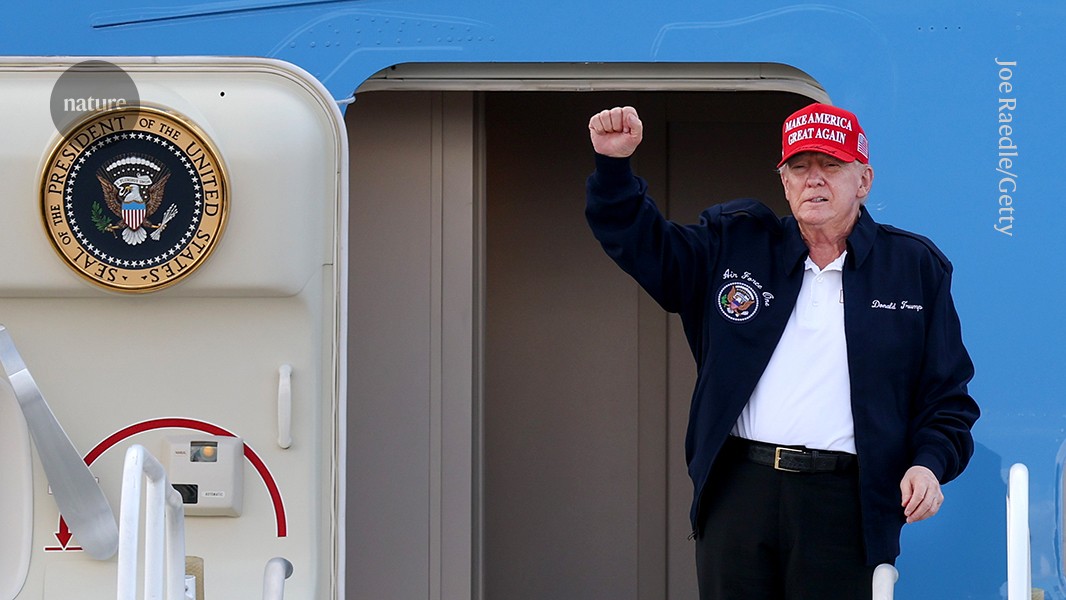
The foundations of America’s prosperity are being dismantled
Federal scientists warn that Americans could feel the effects of the new administration’s devastating cuts for decades to come.

PLOS statement on recent US Executive Orders and scientific integrity - The Official PLOS Blog
Since its founding over twenty five years ago PLOS has been dedicated to advancing open science, ensuring that knowledge is accessible to…
Former CDC director: Two programs reportedly on the chopping block must be saved
Former CDC Director Tom Frieden warns that cutting the Public Health Associate Program and Laboratory Leadership Service risks public safety, especially given the threat of H5N1.

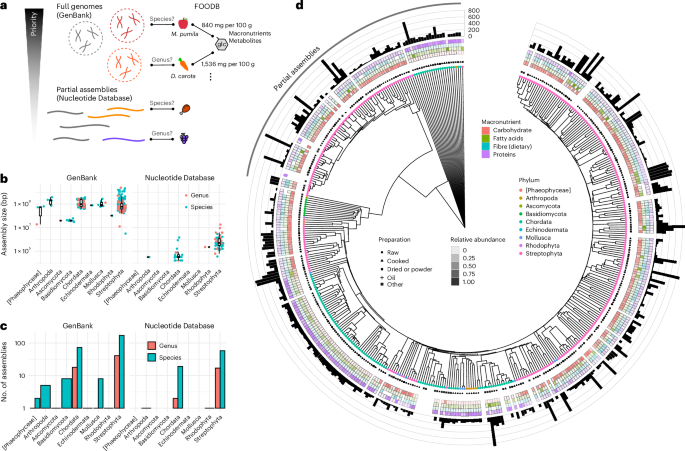
Metagenomic estimation of dietary intake from human stool - Nature Metabolism
Diener et al. present a method that allows the estimation of dietary intake from human stool by detecting food-derived DNA in faecal metagenomes.
AI can now model and design the genetic code for all domains of life with Evo 2 | Arc Institute
Arc Institute develops the largest AI model for biology to date in collaboration with NVIDIA, bringing together Stanford University, UC Berkeley, and UC San Francisco researchers
Trump administration layoffs hit FDA’s device center
The FDA and its Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) were among several health-focused agencies caught in sweeping layoffs over the weekend as the Trump administration seeks | It’s unclear how many staff at the FDA have been affected. There have also been estimates of thousands of dismissals spanning the NIH, the CDC and other agencies across the HHS.

ACLA’s and AMP’s Suits over the LDT Final Rule: Summary Judgement Promised “Soon”
It was an exciting day in Plano, Texas! Yesterday, the Honorable Sean D. Jordan, United States district judge of the United States District Court for the Eastern District of Texas, heard oral argument in the consolidated suits against the U.

Illumina Unveils Spatial Technology Days Before AGBT Meeting
Illumina announces a new NGS-based spatial technology kit and new software platform, Illumina Connected Multiomics.

2024’s top 10 clinical trial flops
Clinical-stage drug development offers big rewards—and big risks. When examining the most high-profile failures of 2024, it becomes obvious how many were in notoriously tricky indications that have been crying out for new therapeutic options, such as Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia and herpes simplex virus. | Fierce Biotech recounts the top 10 clinical trial failures of 2024 that sent ripples across the industry.

AI mirrors experimental science to uncover a novel mechanism of gene transfer crucial to bacterial evolution
AI models have been proposed for hypothesis generation, but testing their ability to drive high-impact research is challenging, since an AI-generated hypothesis can take decades to validate. Here, we challenge the ability of a recently developed LLM-based platform, AI co-scientist, to generate high-level hypotheses by posing a question that took years to resolve experimentally but remained unpublished: How could capsid-forming phage-inducible chromosomal islands (cf-PICIs) spread across bacterial species? Remarkably, AI co-scientist’s top-ranked hypothesis matched our experimentally confirmed mechanism: cf-PICIs hijack diverse phage tails to expand their host range. We critically assess its five highest-ranked hypotheses, showing that some opened new research avenues in our laboratories. We benchmark its performance against other LLMs and outline best practices for integrating AI into scientific discovery. Our findings suggest that AI can act not just as a tool but as a creative engine, accelerating discovery and reshaping how we generate and test scientific hypotheses. ### Competing Interest Statement The authors have declared no competing interest.

AxBio Preps Low-Cost Nanopore Sequencer for Commercial Launch
Semiconductor-based genomics technology startup AxBio is working toward the commercial launch of a long-read, single-molecule nanopore sequencer that promises low cost and high data accuracy for low-throughput applications in research and diagnostics.
Comprehensive benchmarking of methods for mutation calling in circulating tumor DNA
Detection of somatic mutations in cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is challenging due to low variant allele frequencies and pronounced DNA degradation. Here, we present a novel approach and resource for benchmarking of somatic variant calling algorithms in cfDNA samples from cancer patients. Using longitudinally collected cfDNA samples from colorectal and breast cancer patients, we identify patient-matched samples with high and ultra-low circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) levels. These sample pairs, preserving patient-specific germline and somatic haematopoiesis variant backgrounds, were used to generate dilution series capturing characteristics of bona-fide cfDNA samples. To benchmark the accuracy and limit of detection of 9 somatic variant calling algorithms, we used deep Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS, 150x) and ultra-deep Whole Exome Sequencing (WES, 2,000x) to construct a reference set of ~37,000 Single Nucleotide Variants and ~58,000 Insertions/Deletions. We tested methods under variable ctDNA levels and depth of sequencing, generating guidelines for method choice depending on use case. Using a machine learning approach, we further evaluated the potential of fine-tuning individual variant callers, revealing features that may improve accuracy in cfDNA samples. Overall, we present a new resource for benchmarking of somatic variant calling methods in cfDNA, providing insights on method choice to realize the potential of liquid biopsies in precision oncology. ### Competing Interest Statement The authors have declared no competing interest.

Alarm as bird flu now ‘endemic in cows’ while Trump cuts staff and funding
Experts say current US outbreak is unlikely to end without intervention with further mutation of virus likely

Federal Judge Extends TRO Against NIH Cap On Indirect Cost Payments
Federal Judge Angel Kelly has extended her temporary hold on NIH’s plan to cap its payment of indirect research grant costs to 15%.

Trump’s siege of science: how the first 30 days unfolded and what’s next
The breakneck pace and devastating impact of the administration’s policy changes has shocked researchers.